Robotics has seen massive advancements over the past decade, with robots becoming an integral part of industries like manufacturing, healthcare, and logistics. However, the efficiency and performance of robots depend heavily on the power source they use. In this article, we will explore the types of batteries used in robots, how they impact robot performance, and why selecting the right battery is essential for optimizing robotic operations.
Introduction to Robot Batteries
In robotics, the battery serves as the lifeblood of the machine, powering everything from small drones to massive industrial robots. A well-designed battery not only affects a robot’s operating time but also impacts its speed, precision, and ability to perform complex tasks. Given the diversity of robotic applications, the battery requirements vary significantly based on the robot’s functionality, size, and operational environment.
Types of Batteries Used in Robots
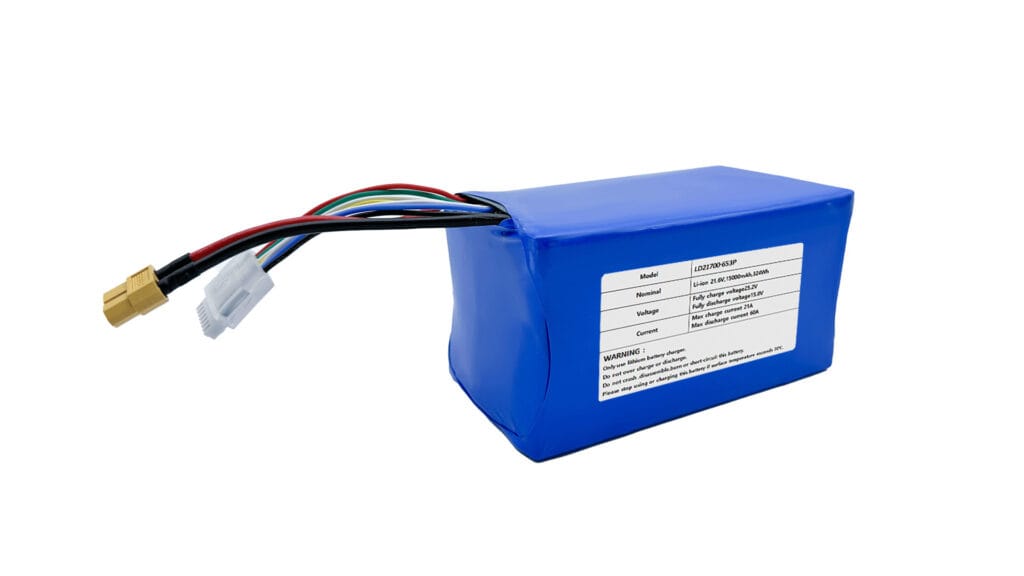
Lithium-Ion (Li-ion) Batteries
Lithium-ion (Li-ion) batteries are the most commonly used power source for robots due to their high energy density, long lifespan, and light weight. These batteries are particularly popular in mobile robots, drones, and autonomous vehicles, where power-to-weight ratio is crucial.
Advantages of Li-ion Batteries:
- High Energy Density: Li-ion batteries offer more power in a compact size, which is essential for mobile robots requiring long operation times.
- Longer Lifespan: With proper care, Li-ion batteries can last for several years, making them ideal for robots that need to operate over long periods.
- Lightweight and Compact: Li-ion batteries have a higher energy-to-weight ratio compared to other battery types, reducing the overall weight of robots.
Disadvantages of Li-ion Batteries:
- Cost: While Li-ion batteries are more efficient, they tend to be more expensive than other options.
- Temperature Sensitivity: Li-ion batteries can be sensitive to temperature fluctuations, requiring cooling systems for some high-performance robots.
Lithium-Polymer (LiPo) Batteries
Lithium-Polymer (LiPo) batteries are a variant of Li-ion batteries. They are used in applications where the robot requires even lighter weight or a more flexible form factor.
Advantages of LiPo Batteries:
- Flexible Design: LiPo batteries can be molded into various shapes, allowing for more customized designs in robots.
- Higher Discharge Rates: LiPo batteries can provide higher discharge rates, which is beneficial for robots that require bursts of power, such as drones or robotic arms in industrial applications.
Disadvantages of LiPo Batteries:
- Fragility: LiPo batteries can be more prone to damage than Li-ion batteries, especially under physical stress.
- Safety Concerns: If punctured or overcharged, LiPo batteries can catch fire or explode.
Solid-State Batteries (Emerging Tech)
Solid-state batteries promise safer, higher-capacity alternatives with faster charging. While not yet mainstream, companies like Toyota are testing them for robotics (IEEE Spectrum, 2022).
Other Battery Technologies
Some advanced robots, especially those used in research or industrial applications, may employ other types of batteries such as Solid-State Batteries or Supercapacitors. These technologies are still in their developmental stages but show great promise in terms of energy efficiency and safety.
How to Choose Battery for Robot
When selecting a battery for a robot, several factors must be considered:
Voltage Requirements: Determine the voltage needs of motors, controllers, and sensors. Ensure the battery’s nominal voltage matches (e.g., 3.7V per cell for Li-ion, 12V for lead-acid). Use series connections to increase voltage or parallel for capacity, ensuring cells are matched.
Capacity (Ah/mAh): Calculate Runtime: Sum the average current draw of all components and multiply by desired runtime (e.g., 2A for 5 hours = 10Ah). Add a 20-30% buffer.
Energy Density: Energy density—the amount of energy stored per unit weight or volume—is the cornerstone of battery selection for mobile robots. Higher energy density translates to longer runtime without adding bulk, which is vital for drones, autonomous delivery robots, or wearable exoskeletons.
Weight and Size: Battery weight directly affects a robot’s mobility, payload capacity, and energy efficiency. For example, aerial drones lose flight time with every added gram, while humanoid robots require compact cells to mimic natural movement.
Cycle Life: Cycle life—the number of charge/discharge cycles before capacity drops to 80%—determines long-term costs. Industrial robots operating 24/7 demand batteries rated for 1,500–3,000 cycles, while consumer robots may settle for 500–1,000 cycles.
Charging Speed: Fast charging minimizes operational interruptions. Logistics robots in e-commerce hubs, for instance, often use 30-minute rapid charging to maintain workflow continuity.
Environmental and Operational Conditions:Robots deployed in extreme environments—from Arctic research stations to steel mills—need batteries that withstand temperature extremes, vibration, and moisture.
Battery Life in Robots
The battery life of a robot is determined by a variety of factors, including the battery capacity, power consumption, and the efficiency of the robot’s systems. Robots designed for short, precise tasks may only require a small battery with a short lifespan, while others designed for continuous operation may require large, high-capacity batteries with longer durations between charges. In most cases, battery life can be optimized through careful design choices, including reducing power consumption in non-essential components or using more efficient motors and actuators.
Looking ahead, the future of robotic batteries is likely to involve further advancements in solid-state battery technology, which promises higher energy densities and greater safety. Other trends include improvements in wireless charging and energy harvesting technologies that could allow robots to recharge autonomously in specific environments.
Custom Battery Solutions for Robots
Custom battery solutions are often necessary for robots that require specialized configurations or performance characteristics. By working with a manufacturer like Lan Dazzle, robotics companies can ensure their robots are powered by batteries designed to meet their specific needs.
Custom batteries allow for tailored solutions that meet specific voltage, size, and weight requirements, while also ensuring optimal energy efficiency. This is especially important in robotics, where one-size-fits-all solutions rarely work.
Lan Dazzle’s Role in Robot Batteries Solutions
Lan Dazzle’s expertise in custom battery manufacturing allows us to provide high-performance, tailored battery solutions for robots in all industries. Whether it’s a compact, lightweight battery for drones or a heavy-duty solution for industrial robots, Lan Dazzle can design and manufacture the perfect power source for your robotic applications.
Conclusion
The choice of battery for robots plays a pivotal role in determining the robot’s performance, efficiency, and longevity. Lithium-ion and lithium-polymer batteries currently dominate the market, but emerging technologies like solid-state batteries hold the potential to reshape the industry. Custom battery solutions, like those offered by Lan Dazzle, ensure that robots are powered by the most effective and reliable energy sources tailored to their specific needs.
Visit https://landazzle.com/robotic/ to learn more about our innovative custom battery solutions.