The type of batteries used in wearable devices plays a crucial role in determining their performance, lifespan, and user experience, and the majority of wearable devices rely on lithium-ion (Li-ion) batteries or lithium-polymer (Li-Po) batteries. In this article, we will explore how shaped batteries can bridge the gap between traditional batteries and empower wearable devices.
Requirements for Wearable Devices Batteries
1. Compact Size: Fitting Power into Tiny Spaces
Wearables prioritize portability, forcing batteries to shrink without sacrificing capacity. For instance, smartwatches like the Apple Watch use slim lithium-polymer (Li-Po) batteries that conform to the device’s curved interior. Similarly, fitness trackers like the Fitbit Charge 6 rely on ultra-thin cells (often as small as 100mAh) to maintain a lightweight profile. Even smart glasses like Ray-Ban Meta tuck tiny batteries into their hinges to avoid bulk.
2. Ergonomic Design: Comfort and Safety First
Batteries must align with the device’s form to prevent discomfort. For example, hearables like wireless earbuds (e.g., AirPods Pro) distribute battery weight evenly across both buds to avoid ear strain. Smart rings like the Oura Ring use flexible, curved batteries that wrap around the finger without sharp edges. Additionally, materials must be skin-safe and heat-resistant, as seen in medical wearables like continuous glucose monitors, where direct skin contact is constant.
3. Energy Efficiency: Maximizing Runtime in Minimal Space
With limited room for large cells, wearables demand batteries with high energy density. The Garmin Fenix 7 smartwatch, for example, uses advanced Li-Po cells to deliver weeks of battery life despite its GPS and health-tracking features. Similarly, AR glasses like Xreal Air 2 rely on optimized power management to balance display brightness and battery drain.
Type of Batteries Used in Wearable Devices
1. Lithium-Ion (Li-ion) Batteries
- Energy Density: ~250–300 Wh/kg (typical for small cells).
- Cycle Life: 300–500 cycles (capacity drops to 80%).
- Safety: Risk of leakage or thermal runaway if damaged.
- Cost: Lower than Li-Po, widely available.
- Applications: Older wearables (e.g., early Fitbit models).
2. Lithium Polymer (Li-Po) Batteries
- Energy Density: ~250–300 Wh/kg (similar to Li-ion but more flexible in shape).
- Cycle Life: 400–600 cycles.
- Safety: Safer than Li-ion due to gel electrolyte; lower leakage risk.
- Cost: Slightly higher than Li-ion.
- Applications: Dominant in modern wearables (e.g., Apple Watch Series 8, Galaxy Watch 5).
3. Solid-State Batteries
- Energy Density: 400–500 Wh/kg (projected for wearables).
- Cycle Life: 1,000+ cycles (experimental stages).
- Safety: Non-flammable electrolyte; no leakage risk.
- Cost: Currently 2–3x higher than Li-Po.
- Applications: Prototypes only (e.g., experimental hearables by startups like Solid Power).
Comparison Table
| Parameter | Lithium-Ion (Li-ion) | Lithium Polymer (Li-Po) | Solid-State |
|---|---|---|---|
| Energy Density | 250–300 Wh/kg | 250–300 Wh/kg | 400–500 Wh/kg (projected) |
| Cycle Life | 300–500 cycles | 400–600 cycles | 1,000+ cycles (R&D) |
| Flexibility | Rigid | Flexible shape | Customizable |
| Safety | Moderate | High | Very High |
| Cost (per kWh) | 100–100–150 | 120–120–180 | 300–300–500 (current) |
| Example Use | Early Fitbit models | Apple Watch, Galaxy Watch | Prototypes (e.g., Solid Power) |
Why Li-Po Dominates Wearables Today
Li-Po batteries dominate due to their flexibility in design, improved safety, and balance of cost and performance. For example, the Apple Watch Series 8 uses a 1.11 Wh Li-Po cell for its slim profile (iFixit Teardown, 2022).
Solid-state batteries promise a future leap in energy density and safety but remain limited by manufacturing costs and scalability challenges. Companies like QuantumScape are targeting wearables as a niche market for early adoption (QuantumScape, 2023).
Shaped Batteries: Overcoming Traditional Limitations in Wearables
The rapid growth of wearable technology—from fitness trackers to AR glasses—demands batteries that are not only compact but also adaptable to unconventional designs. Traditional cylindrical or rectangular batteries often fall short in meeting these needs. This is where custom-shaped batteries shine, offering tailored solutions that address the unique challenges of wearable devices. Let’s explore how these innovative power sources outperform conventional options, with real-world examples across smart rings, glasses, and more.
Limitations of Traditional Batteries in Wearables
- Shape Rigidity: Cylindrical or prismatic batteries restrict design flexibility, forcing wearables to compromise on aesthetics or ergonomics.
- Space Inefficiency: Fixed shapes leave “dead spaces” in compact devices, reducing potential battery capacity.
- Safety Concerns: Rigid casings can struggle to withstand bending or impact in dynamic wearables.
- Thickness Issues: Bulky batteries conflict with the slim profiles required for comfort.
How Custom-Shaped Batteries Solve These Problems
1. Design Freedom for Space Optimization
Custom-shaped batteries are molded to fit the exact contours of a device, eliminating wasted space. For example:
- Smart Rings: A circular or curved battery can wrap around the ring’s inner surface, maximizing capacity without increasing bulk. Case Study: A leading smart ring brand achieved 3-day battery life in a 5mm-thick design using a crescent-shaped lithium polymer battery.
- AR Glasses: Ultra-thin batteries (as slim as 0.45mm) can integrate into the frame’s temples, enabling all-day use without compromising weight distribution.
2. Enhanced Safety with Flexible Encapsulation
Unlike rigid metal casings, custom batteries use lightweight, bendable laminated materials (e.g., aluminum-plastic film). This makes them ideal for:
- Fitness Bands: Curved batteries withstand repeated flexing during workouts.
- Hearables: Soft-pack batteries reduce risks of leakage or rupture in sweat-prone earbuds.
3. Higher Energy Density via Structural Innovation
By filling every millimeter of available space, custom batteries deliver up to 30% more capacity than standard counterparts. For instance:
- Medical Patches: A zigzag-shaped battery in a glucose monitor extended runtime to 7 days, critical for continuous health tracking.
4. Ultra-Slim Profiles for Discreet Wearables
Custom batteries enable sleek, ergonomic designs:
- Smart Eyewear: A 0.6mm-thick battery embedded in the nose bridge powers a micro-display for 8+ hours.
- Luxury Smartwatches: Irregularly shaped cells follow the curve of high-end watch cases, preserving iconic aesthetics.
Real-World Applications
-
Smart Ring Powering Gesture Control
A gaming-focused smart ring uses a C-shaped battery to power its motion sensors and haptic feedback. The design allows seamless integration into a 7mm-wide ring, supporting 48 hours of active use
-
Fitness Tracker with Curved Battery
A popular fitness band features a curved 120mAh battery that follows the wrist’s natural contour, adding 20% capacity versus a rectangular cell of the same volume.
-
Military-Grade AR Glasses
Custom L-shaped batteries in tactical glasses provide 12 hours of thermal imaging and HUD operation, withstanding extreme temperatures and vibrations.
How Shaped Batteries Empower Next-Generation Wearable Devices
As wearable technology evolves — from smartwatches and fitness trackers to AR glasses and medical sensors — the demand for batteries that adapt to innovation grows exponentially. While lithium-ion batteries dominate the consumer electronics market, shaped batteries are emerging as the silent enablers of cutting-edge wearable designs
Why Shaped Batteries Are Revolutionizing Wearables
-
Form Factor Freedom
Traditional rectangular or coin-cell batteries force engineers to design devices around the battery. Shaped batteries invert this paradigm. By conforming to curves, hollow spaces, or irregular geometries (e.g., ring-shaped batteries for smart jewelry), they unlock unprecedented design flexibility. Example: A health-monitoring ring can now house a crescent-shaped battery that follows the device’s contour, maximizing internal space for sensors without compromising comfort.
-
Space Optimization = Enhanced Functionality
Wearables thrive on miniaturization. A 2023 teardown study revealed that devices using shaped batteries allocate 15-30% more space to critical components (e.g., biometric sensors, processors) compared to those with standard batteries. This directly translates to smarter, lighter, and more feature-rich products.
-
Energy Density Tailored to Unique Needs
Shaped batteries aren’t just about aesthetics — they’re engineered for performance. Through advanced stacking and electrode customization, these batteries achieve higher energy density in targeted zones. For instance, a curved battery in AR glasses can prioritize power delivery to the display module while maintaining a slim profile
-
Durability Meets Wearability
Flexible substrates and encapsulation materials allow shaped batteries to withstand bending (e.g., in foldable fitness bands) and repetitive motion. A case study by a leading smart clothing brand showed a 40% longer cycle life for shaped batteries in washable garments versus rigid alternatives.
Real-World Applications Redefined
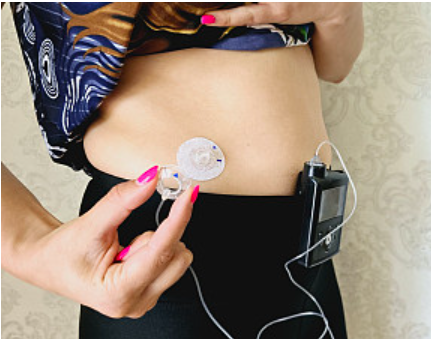
- Medical Wearables: ECG patches with ultra-thin, skin-adherent batteries for 7-day continuous monitoring.
-
Fashion-Tech Hybrids: Designer smartwatches with batteries molded into bracelet links, eliminating “bulge” aesthetics.
-
Athletic Gear: Pressure-sensitive insoles powered by foot-shaped batteries that harvest kinetic energy.
What to Look for in a Wearable Device Battery: A Buyer’s Guide
As wearable devices become essential tools for health tracking, communication, and productivity, their batteries play a pivotal role in defining user experience. Beyond brand specs and flashy features, here’s what truly matters when evaluating a wearable’s battery performance:
1. Battery Life vs. Device Size: Striking the Balance
A slim fitness band boasting “7-day battery life” may hide compromises. Key questions to ask:
- Energy density: How much power (mAh) is packed into the battery’s volume? Higher density = longer runtime without bulk.
- Efficiency: Does the device optimize energy use via low-power processors or sleep modes?
Why shaped batteries matter: Custom-shaped designs (e.g., curved or stacked cells) maximize energy storage in tight spaces, enabling longer life in sleek form factors like smart rings or AR glasses.
2. Charging Speed & Convenience
Frequent charging kills usability. Prioritize:
- Fast-charging tech: Can 10 minutes of charging deliver a full day’s use?
- Wireless/contactless options: Critical for waterproof devices (e.g., swim trackers).
Shaped battery innovation: Flexible batteries enable integrated wireless charging coils, reducing internal space conflicts.
3. Safety & Durability
A battery should survive daily wear-and-tear. Verify:
- Certifications: UL/IEC standards for heat resistance, overcharge protection.
- Bendability: For devices worn on joints (e.g., knee straps), batteries must withstand 10,000+ flex cycles.
Case in point: Medical wearables use ultra-thin, bendable batteries with flame-retardant encapsulation for skin-safe operation.
4. Shape & Space Adaptability
A bulky battery ruins ergonomics. Look for:
- Space-efficient integration: Does the battery conform to the device’s geometry (e.g., ring-shaped, curved)?
- Weight distribution: Heavy batteries cause discomfort in earables or VR headsets.
Shaped battery advantage: Custom molds let batteries fill “dead spaces” (e.g., smartwatch straps), freeing up room for larger screens or sensors.
5. Sustainability & Longevity
Avoid devices that need yearly replacements. Check:
- Cycle life: A good wearable battery retains ≥80% capacity after 500 cycles.
- Recyclability: Are materials like lithium-cobalt or solid-state electrolytes eco-friendly?
Pro tip: Shaped batteries with modular designs (e.g., replaceable cells in hearing aids) extend device lifespans.
The future of custom-shaped batteries lies in their ability to become invisible—not just physically, but also in how seamlessly they integrate into our lives. From smart rings that never need charging to medical devices that monitor health from inside the body, shaped batteries will unlock unprecedented innovation. For wearable manufacturers, staying ahead means embracing these advancements today—partnering with battery innovators, investing in R&D, and reimagining what’s possible when form truly meets function.
Lan Dazzle: Empower Custom Battery Solutions
Designed for medical devices, IoT sensors, and wearable technology, Lan Dazzle’s lightweight lithium batteries combine ultra-low profile (as thin as 0.6mm) and customizable shapes to fit compact spaces. With high energy density (250-300Wh/kg) and stable discharge, they power smartwatches, implantables, wireless trackers, and medical monitors. Enhanced safety features (temperature resistance, puncture protection) ensure reliability in sensitive environments.