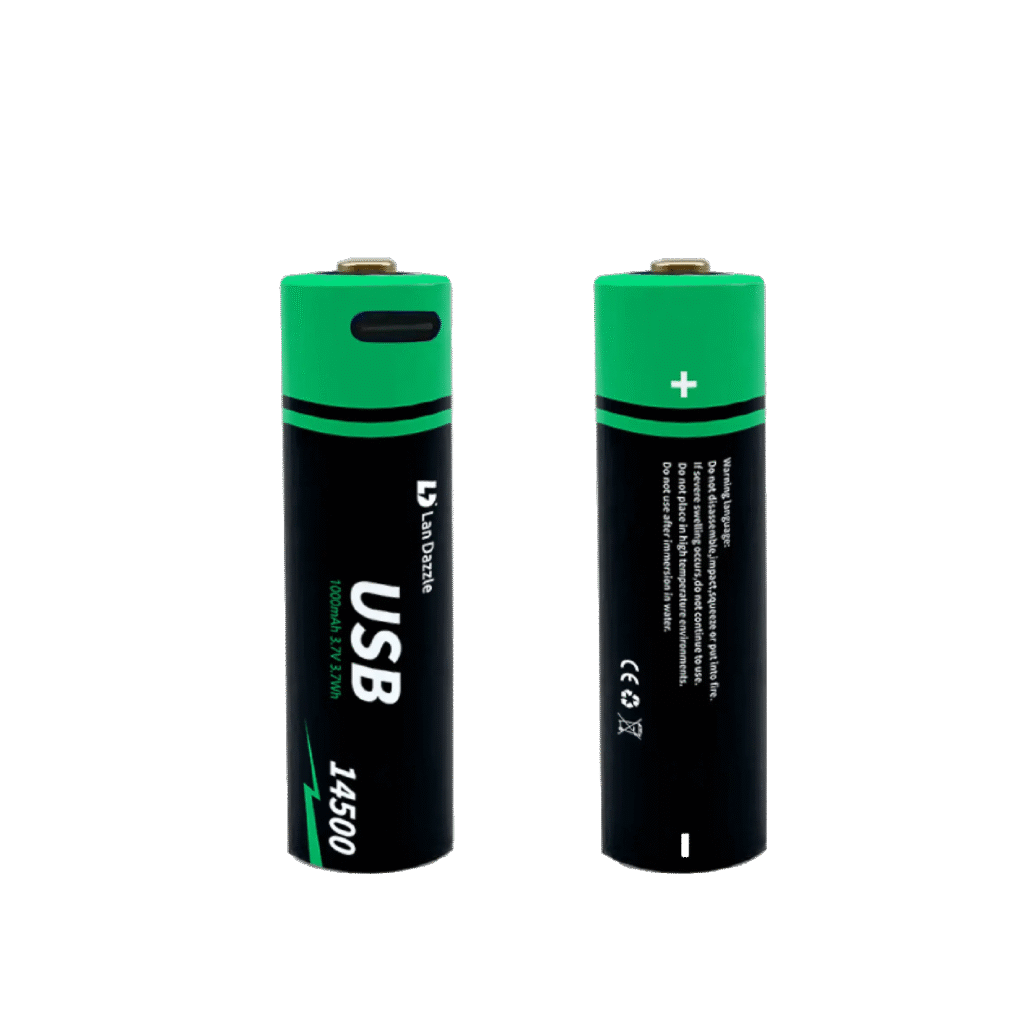
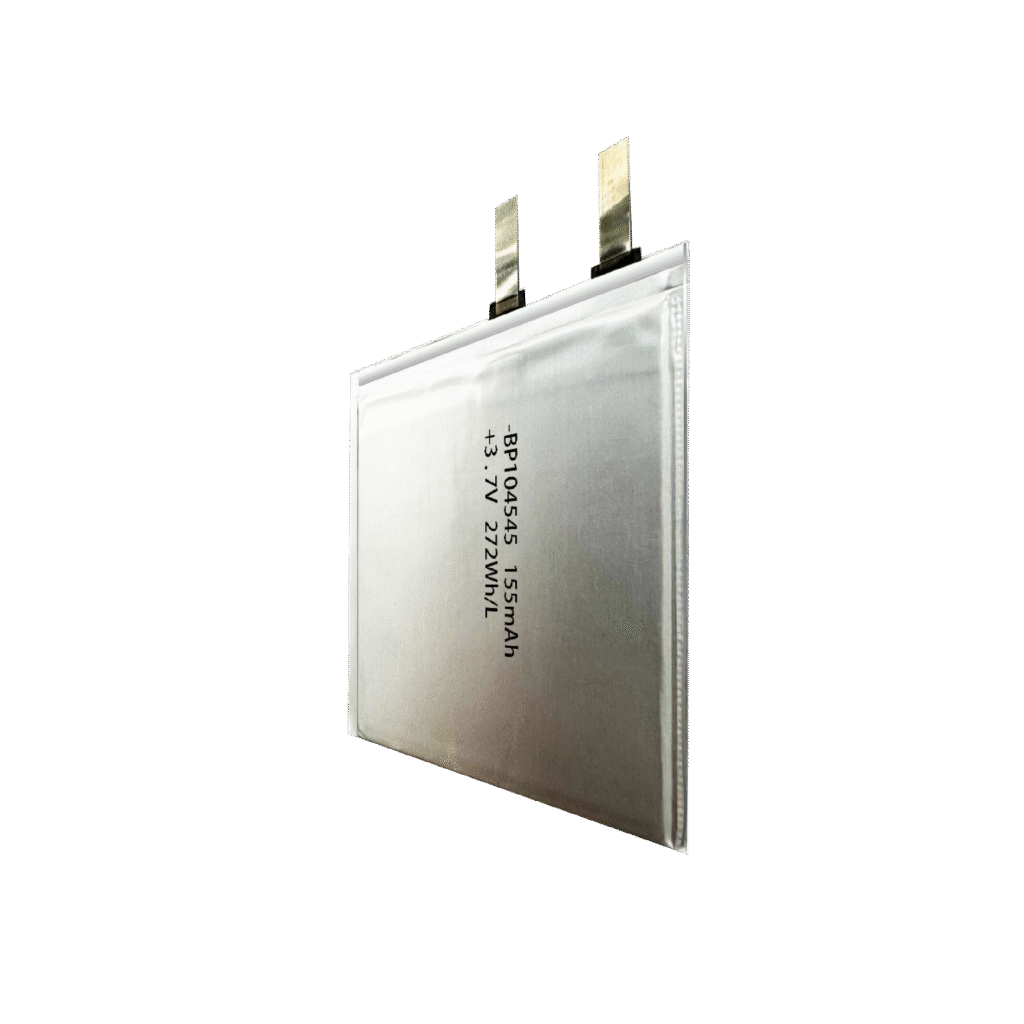
Custom Lipo Battery Manufacturer

BluePower-Custom Shaped Lipo Battery Manufacturer
We specialize in designing and manufacturing custom-shaped batteries to fit the unique demands of cutting-edge industries. With 20+ battery experts and a global team of 200+ professionals, we deliver precision-engineered solutions for:
- Medical Devices (e.g., implantable sensors, portable diagnostics)
- Robotics (flexible batteries for agile movement)
- IoT & Wearables (ultra-compact, long-lasting power)
- Consumer Electronics (slim, high-capacity designs)
Why Trust Us?
✅ Proven Expertise: Successfully completed 1,000+ bespoke projects for clients in 20+ countries, including Fortune 500 companies.
✅ R&D Excellence: 15% annual revenue reinvested in innovation, resulting in 50+ patents.
✅ Compliance & Safety: Certified to meet ISO 13485 (medical), UN38.3, and IEC 62133 standards.
From concept to mass production, we transform spatial constraints into competitive advantages.
- |
- Our Advantages
How Can We Help?
Custom Battery Design
Rapid Prototyping
Engineering Support
Certification Support
Specific Solutions
- |
- Certification
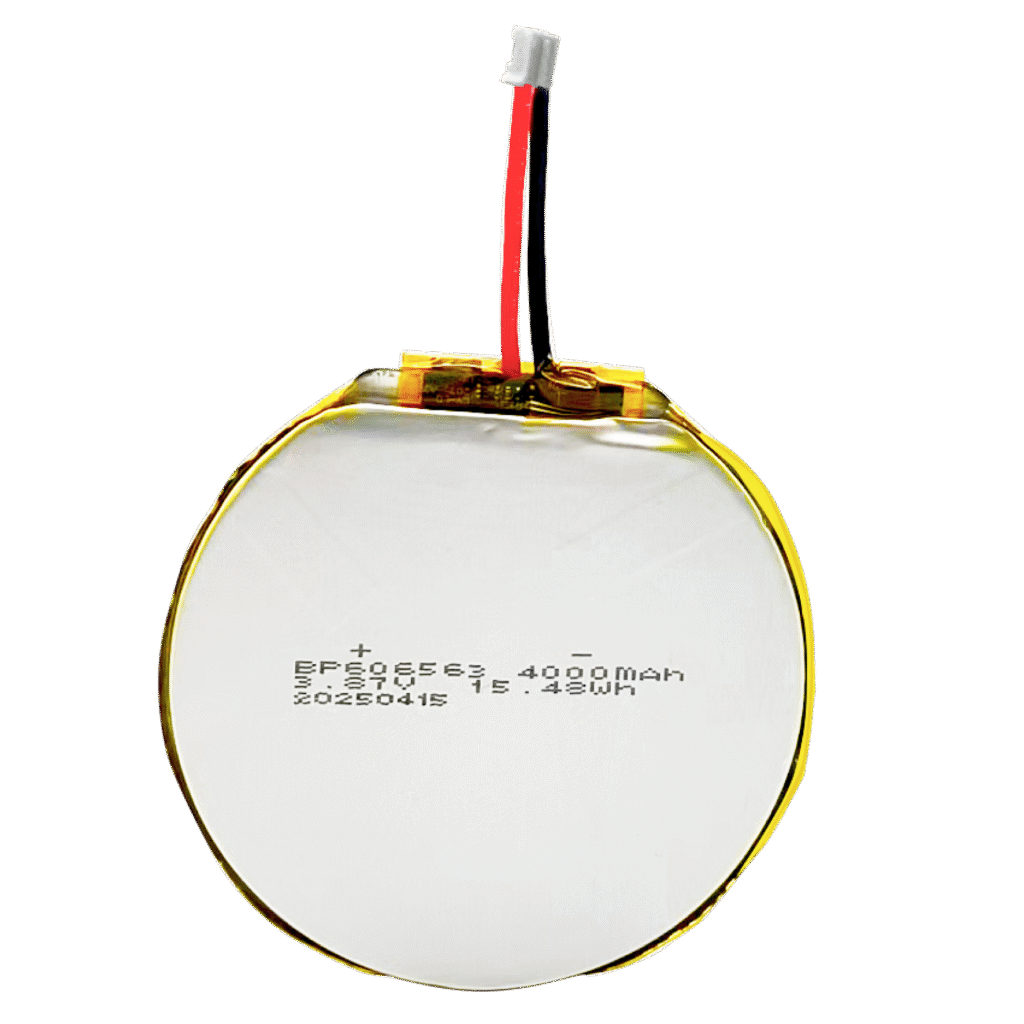
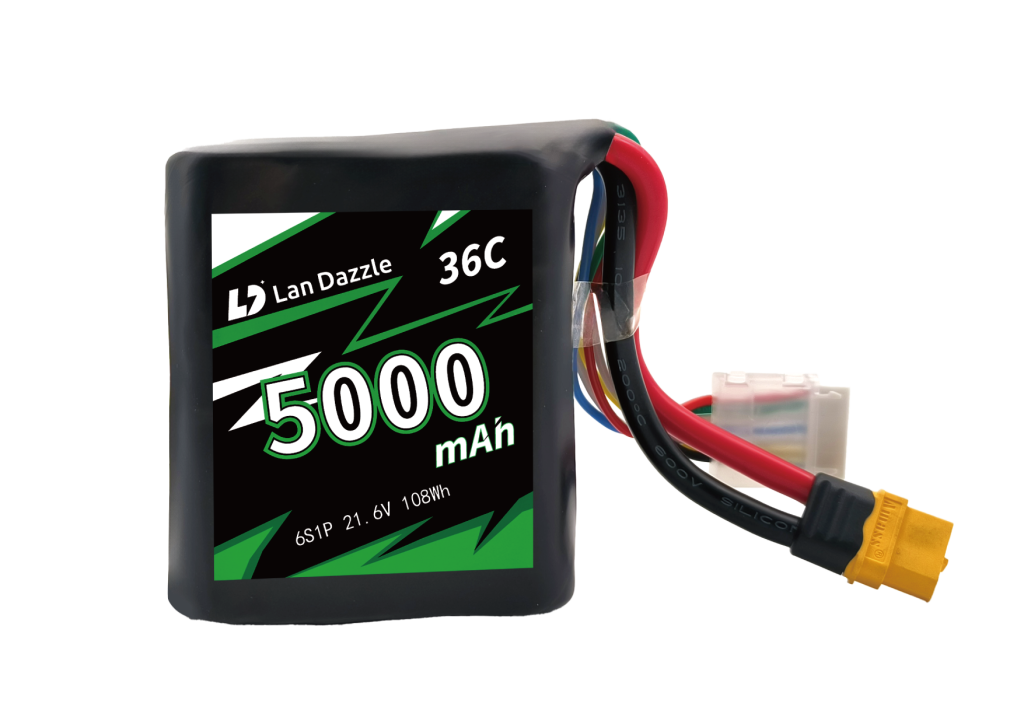
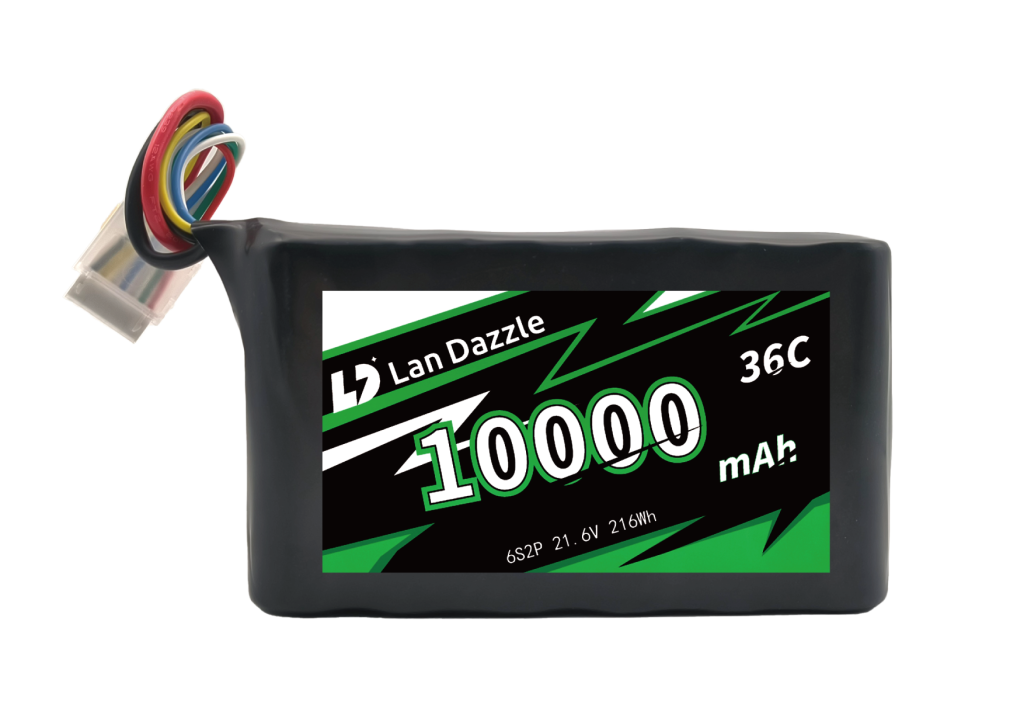
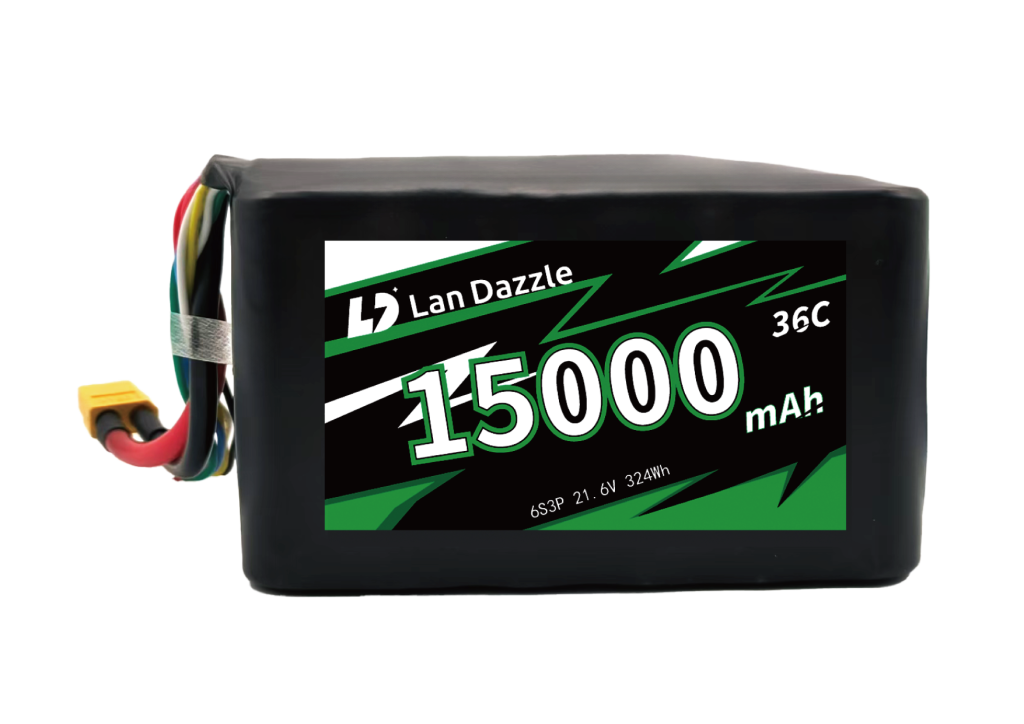
Custom Shaped Battery Manufacturer
ISO 9001; ISO14001; ISO45001; UN38.3; UL; KC; CB; BIS, IEC62133








- |
- Contact us
Request a Quote
We’re here to help.
Battery performance is never one-size-fits-all. Standard options fail when precision and reliability are critical.
We engineer every cell and pack with the expertise to remove uncertainty from your power design.
Start your custom project today.
- |
- Why choose us
How We Provide Value

Customized Design
Custom Battery Based on Your Requirments
We design every battery around your exact specifications—size, capacity, voltage, and performance.
Whether you need a compact cell or a complex battery pack, our engineering team ensures a perfect fit for your application.
We provide battery solutions for many sectors like
- Wearables devices
- Medical devices
- IoT devices
- Drones and UAVs
Customized Design
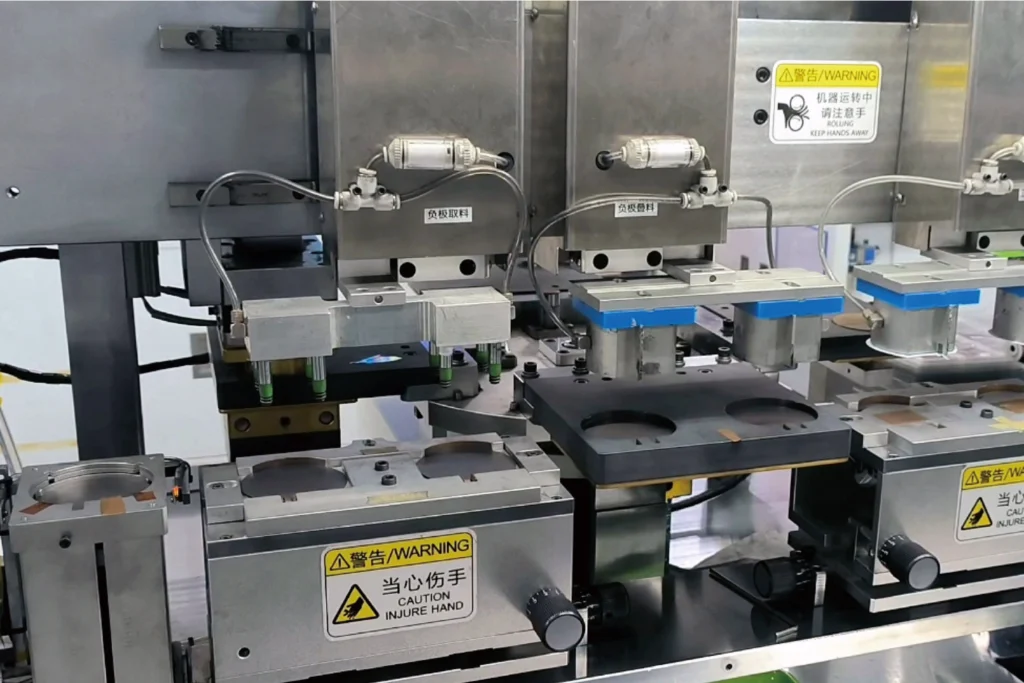
Accelerated Prototyping
We believes that rapid prototyping is key to faster product development.
We dedicate specialized resources and advanced tools to shorten the design-to-validation cycle.
Accelerated prototyping helps our customers reduce risk, refine their designs early, and speed up time-to-market.


Customized Design
Expertise in Battery Engineering
We have built a highly experienced engineering team to ensure every battery solution meets the highest technical standards.
Our expertise is backed by years of practical experience in lithium battery design, manufacturing, and application integration.
Provide deep knowledge of battery chemistry and performance optimization
Translate complex technical requirements into practical solutions
Focus on reducing design risks and ensuring product reliability
Support customers from concept through to mass production
Customized Design
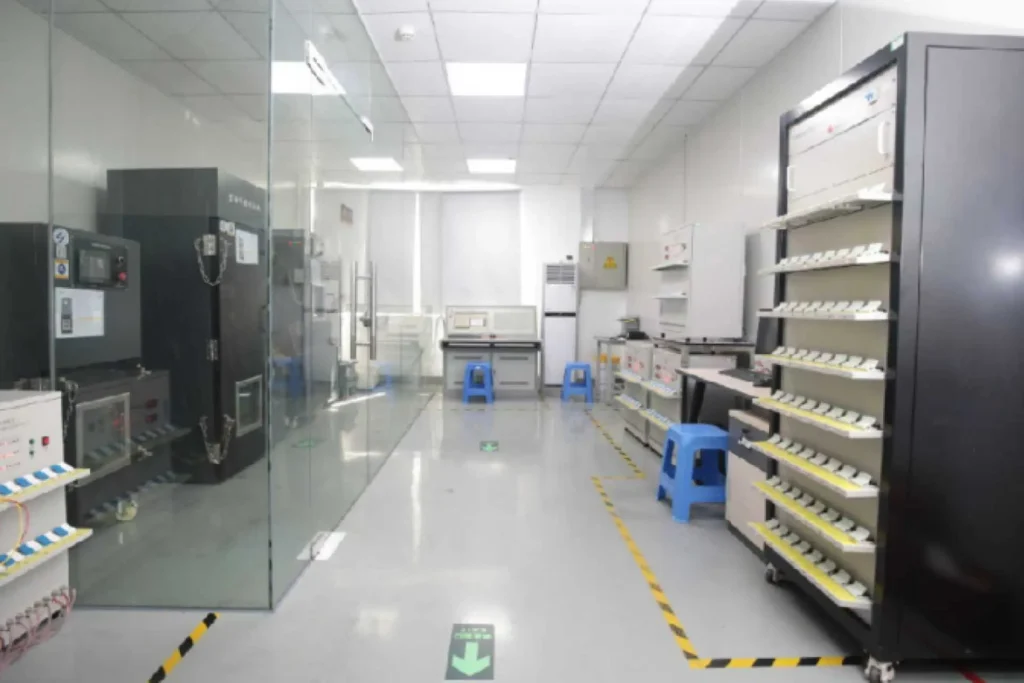
Quality Control Ensures Reliability
Our quality philosophy ensures every battery meets the highest performance and safety standards.
Rigorous inspection – We implement strict testing at every stage, from raw materials to finished products.
Process discipline – Standardized procedures ensure consistency and repeatability in every production run.
Defect prevention – We focus on proactive measures to eliminate issues before they reach the customer.
Continuous improvement – We regularly review quality data and refine our processes for even better results.

- |
- Our Partner