The Hidden Dangers: Can You Use a Damaged Lithium Battery?
That nagging feeling when your phone gets unusually hot, or the slight bulge you’ve noticed on your laptop battery – these are often subtle clues that something might be amiss. Lithium batteries have become the unsung heroes powering our modern lives, from smartphones and laptops to electric vehicles and power tools. But like any technology, they can be susceptible to lithium battery damage.
This brings us to a critical question: can I use a damaged lithium battery? The short answer, and the one we’ll explore in detail, is a resounding NO. Ignoring the warning signs and continuing to use a compromised battery can lead to serious consequences, putting yourself, your devices, and your surroundings at risk. (Seven things you need to know about lithium-ion battery safety)
Understanding the Anatomy of a Lithium Battery
To truly understand the dangers, it’s helpful to have a basic grasp of what’s inside these powerhouses. A typical lithium battery consists of four main components: the cathode (the positive electrode), the anode (the negative electrode), an electrolyte (a chemical substance that allows ions to flow between the electrodes), and a separator (a thin barrier preventing direct contact between the cathode and anode). Think of it like a carefully orchestrated dance of ions. When the battery is working correctly, lithium ions move smoothly between the anode and cathode during charging and discharging. However, this delicate balance can be easily disrupted by physical damage, internal faults, or even improper usage, potentially leading to cell degradation.
Click What Causes Lithium Batteries to Swell? to learn more details about damaged lithium battery.
Identifying the Tell-Tale Signs of a Damaged Lithium Battery
Recognizing the signs of damaged battery is the first line of defense. Here are some key indicators to watch out for:
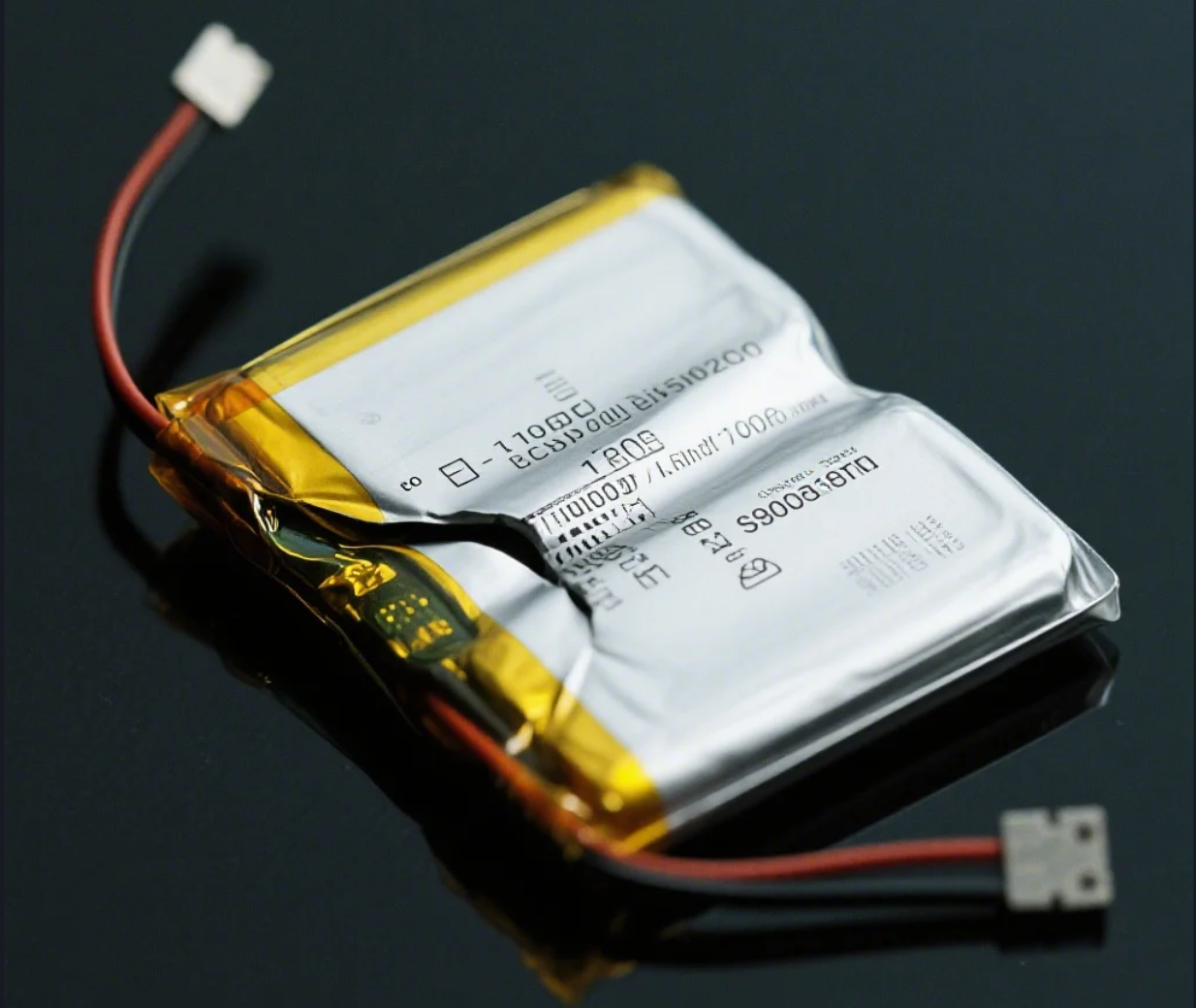
- Physical Damage: This is often the most obvious sign. Look for dents, cracks, or punctures on the battery casing. Pay particularly close attention to swelling or bulging (a key indicator of a swollen lithium battery). If your battery looks like it’s inflated, even slightly, stop using it immediately. Also, be aware of any leaking fluid or corrosion on the battery terminals.
- Functional Issues: How the battery behaves can also signal trouble. Does your device overheat significantly during use or while charging? Does the battery drain much faster than usual? Is it unable to charge fully, or does it die unexpectedly even when showing a decent charge? Unusual hissing or popping sounds coming from the battery are also serious red flags, potentially indicating thermal runaway.
- Visual Cues: Besides physical damage, look for any discoloration of the battery casing.
Imagine your smartphone battery looks like it’s slightly inflated – almost pillow-like. This swelling indicates the production of gas inside the battery, a direct result of internal chemical reactions going awry. Continuing to use a battery in this condition is like playing with fire, increasing the battery fire hazard.
The Hidden Dangers: Why Using a Damaged Lithium Battery is Risky
The risks of damaged lithium battery are significant and should never be underestimated. The most serious dangers include:
- Risk of Fire: One of the most concerning risks is thermal runaway. This is a chain reaction within the battery where heat builds up uncontrollably, leading to fire or even explosion. Damage to the battery, such as a puncture or internal short circuit, can trigger this dangerous process. According to some reports, battery-related fires have been on the rise in recent years, highlighting the importance of vigilance regarding battery safety.
- Risk of Explosion: Internal damage can also cause a build-up of pressure within the battery. If this pressure exceeds the battery’s structural integrity, it can result in a violent explosion, potentially causing serious injury and property damage. There have been numerous documented cases of devices exploding due to damaged batteries, serving as stark reminders of the potential consequences and the battery explosion risk.
- Release of Toxic Fumes: Damaged lithium batteries can leak harmful chemicals and release toxic fumes. Inhaling these fumes can be dangerous to your health.
- Damage to Devices: A faulty battery can also damage the device it’s powering. Voltage fluctuations or internal shorts can fry sensitive electronic components.
- Personal Injury: The potential for burns, injuries from explosions, and inhalation of toxic fumes makes using a damaged lithium battery a significant personal safety hazard.
What to Do If You Suspect Your Lithium Battery is Damaged
If you suspect your lithium battery damage, immediate action is crucial. Here’s what you should do:
- Stop Using It Immediately: This is the most important step. Do not continue to use the device or the battery.
- Do Not Attempt to Charge It: Charging a damaged battery can further destabilize it and increase the risk of fire or explosion.
- Handle with Care: Avoid dropping the battery or subjecting it to any further physical stress.
- Isolate the Device: Place the device or battery on a non-flammable surface, away from combustible materials.
- Proper Disposal: Never throw a damaged lithium battery in the regular trash or recycling bin. Take it to a designated battery disposal or a collection point often found at electronics stores. Improper disposal can lead to environmental contamination and safety hazards.
- Seek Professional Advice: If you’re unsure about the condition of your battery or how to handle it, contact the device manufacturer or a qualified technician for guidance.
Prevention is Key: Extending the Life and Safety of Your Lithium Batteries
Preventing damage in the first place is the best way to ensure the battery safety and longevity of your lithium batteries. Here are some essential tips:
- Use the Correct Charger: Always use the charger specifically designed for your device or battery. Using incompatible chargers can lead to overcharging and damage.
- Avoid Extreme Temperatures: Both excessive heat and extreme cold can negatively impact battery lifespan and performance. Don’t leave devices in direct sunlight or freezing temperatures.
- Protect from Physical Impact: Be careful not to drop your devices or subject batteries to pressure. Even seemingly minor impacts can cause internal damage.
- Don’t Overcharge: While modern devices often have mechanisms to prevent overcharging, it’s still good practice to unplug them once they reach full charge.
- Store Properly: If you’re not going to use a device or battery for an extended period, store it in a cool, dry place with a partial state of charge (SoC) (around 50%).
Conclusion
The message is clear: never use a damaged lithium battery. The potential dangers of using damaged battery, including battery fire hazard and battery explosion risk, far outweigh any perceived convenience. By understanding the signs of damaged battery, knowing how to handle a compromised battery safely, and taking preventative measures, you can protect yourself, your belongings, and the environment. When in doubt, always err on the side of caution and replace the battery. Your safety is worth it.
FAQ
- Is it ever safe to use a lithium battery that looks slightly swollen? (Answer: Absolutely not. Swelling is a major sign of internal damage and can lead to fire or explosion.)
- What should I do if my lithium battery gets wet? (Answer: Stop using it immediately, handle it with care, and dispose of it properly at a recycling center. Water can cause short circuit and corrosion.)
- Can a damaged lithium battery be repaired? (Answer: Generally, no. Attempting to repair a damaged lithium battery is extremely dangerous and not recommended. It’s best to replace it.)
- How do I properly dispose of a damaged lithium battery? (Answer: Do not throw it in the regular trash or recycling bin. Take it to a designated battery recycling center or a collection point at electronics stores.)
- My phone battery gets hot sometimes. Is that a sign of damage? (Answer: While occasional mild warmth during heavy use or charging is normal, excessive or frequent overheating could indicate a problem and should be monitored closely. If it’s consistently hot or swollen, stop using it.)
- Can I still use my device if the battery has a small dent? (Answer: Even minor physical damage like a dent can compromise the internal structure and battery safety. It’s best to err on the side of caution and replace it.)