In our increasingly mobile and gadget-filled world, batteries are the unsung heroes powering our daily lives. From the smartphones in our pockets to the drones soaring in the sky, a specific type of battery has become incredibly prevalent: the LiPo battery, short for lithium polymer battery. If you’re new to the world of electronics or simply curious about what makes these batteries so popular, you’ve come to the right place. This beginner-friendly guide will break down everything you need to know about LiPo cells, explaining what they are, how they work, their advantages, safety considerations, and where you might encounter them.
What Exactly Are LiPo Cells?
At its core, a LiPo battery is a type of rechargeable battery that utilizes lithium-ion technology. What sets it apart from traditional lithium-ion batteries is the use of a polymer electrolyte instead of a liquid electrolyte. Think of the electrolyte as the medium that allows the flow of electrically charged particles (lithium ions) within the battery. In a LiPo battery, this electrolyte is a gel-like or solid polymer, giving the battery several unique characteristics.
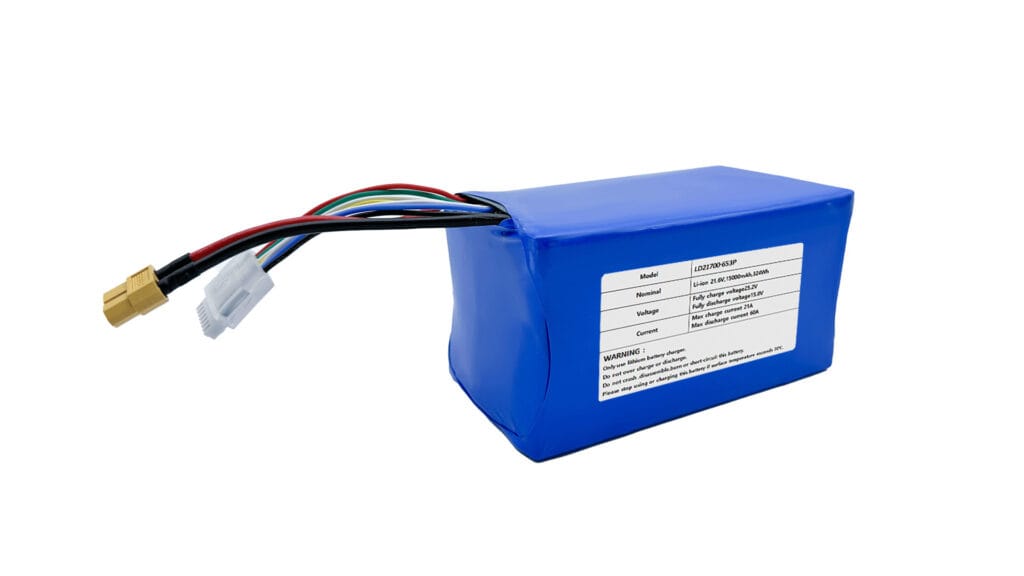
Like all batteries, a LiPo cell consists of four main components: a positive electrode (cathode), a negative electrode (anode), a separator, and the electrolyte. The polymer electrolyte in LiPo batteries is typically a thin, flexible sheet, which allows manufacturers to create batteries in a wide variety of shapes and sizes. This flexibility in form factor is one of the key advantages that has made LiPo batteries so popular in modern, compact devices. A single LiPo cell typically has a nominal voltage of 3.7V.
How Do LiPo Batteries Work?
The magic of a LiPo battery lies in the movement of lithium ions between the anode and the cathode. When you charge a LiPo battery, an external power source forces lithium ions to move from the cathode (usually made of lithium metal oxide) to the anode (typically made of graphite). These ions are stored in the anode. When you use the battery to power a device (discharge), the lithium ions flow back from the anode to the cathode through the electrolyte, releasing energy in the process.
The polymer electrolyte plays a crucial role in this process. It not only facilitates the movement of lithium ions but also acts as a separator between the anode and cathode, preventing them from touching and causing a short circuit. This solid or gel-like nature of the electrolyte contributes to the thin and flexible design of LiPo batteries. While the detailed chemistry can get quite complex, understanding this basic movement of ions is key to grasping how LiPo batteries function.
Advantages of LiPo Batteries
LiPo batteries have become the go-to power source for many applications due to their numerous advantages:
- Lightweight and Compact: One of the most significant benefits is their high energy density to weight ratio. This means they can store a significant amount of energy for their size and weight, making them ideal for portable electronics where every gram counts.
- Flexible Shapes and Sizes: Unlike traditional cylindrical or prismatic batteries, LiPo batteries can be manufactured in almost any shape and size. This allows designers to create sleek and compact devices that fit comfortably in our hands or can be integrated into complex designs like drones.
- Higher Energy Density: Compared to older battery technologies like Nickel-Cadmium (NiCad) or Nickel-Metal Hydride (NiMH), LiPo batteries generally offer higher energy density. This translates to longer battery life for a given size and weight.
- High Discharge Rates: LiPo batteries can deliver high bursts of power, which is essential for applications like drones that require sudden increases in motor speed or RC vehicles needing quick acceleration. This ability is often quantified by the “C-rate.”
- Relatively Low Self-Discharge: When not in use, LiPo batteries tend to lose their charge at a slower rate compared to some other battery types, meaning your device will likely be ready to go even after sitting on the shelf for a while.
Disadvantages and Safety Considerations of LiPo Batteries
Despite their advantages, LiPo batteries also have some drawbacks and require careful handling:
- Sensitivity to Overcharging and Over-Discharging: LiPo batteries are sensitive to being charged beyond their maximum voltage or discharged below their minimum voltage. This can lead to damage, reduced lifespan, or even safety hazards. This is why devices using LiPo batteries often incorporate a Battery Management System (BMS) to prevent overcharging and over-discharging.
- Potential for Swelling and Thermal Runaway: If damaged, improperly handled, or subjected to extreme temperatures, LiPo batteries can swell due to the release of gases. In severe cases, this can lead to a dangerous condition called thermal runaway, which can result in fire or explosion.
- Shorter Lifespan Compared to Some Other Batteries: While constantly improving, the cycle life (number of times a battery can be charged and discharged) of LiPo batteries can be shorter compared to some other battery chemistries. Typical LiPo batteries might offer around 300-500 charge-discharge cycles before their capacity starts to significantly decrease.
- Higher Cost Compared to Older Technologies: Generally, LiPo batteries tend to be more expensive to manufacture than older battery technologies.
- Specific Storage Requirements: LiPo batteries need to be stored properly to maintain their health and safety. Extreme temperatures and storing them at very high or very low charge levels for extended periods can be detrimental.
Applications of LiPo Batteries
The versatility and performance of LiPo batteries have made them indispensable in a wide range of applications:
- Consumer Electronics: You’ll find LiPo batteries powering most modern smartphones, tablets, laptops, and portable gaming consoles due to their slim design and high energy density.
- Hobbyist Use: LiPo batteries are extremely popular in the world of drones, RC cars, airplanes, and other remote-controlled vehicles due to their lightweight nature and ability to deliver high power.
- Wearable Technology: Smartwatches, fitness trackers, and other wearable devices rely on the compact and flexible nature of LiPo batteries.
- Portable Power Banks: Many portable chargers use LiPo batteries to provide a lightweight and high-capacity power source for charging other devices on the go.
- Some Electric Vehicles: While larger electric vehicles often use different lithium-ion configurations, some smaller electric scooters, bikes, and even some cars utilize LiPo technology.
Caring for Your LiPo Batteries
Proper care is essential to maximize the lifespan and safety of your LiPo batteries:
- Use the Correct Charger: Always use a charger specifically designed for LiPo batteries. Using the wrong charger can lead to overcharging and damage.
- Avoid Overcharging: Don’t leave your LiPo batteries charging for extended periods after they are full. Many modern devices have built-in protection circuits, but it’s still good practice to unplug them when charging is complete.
- Avoid Complete Discharge: Try not to let your LiPo batteries completely drain. Regularly charging them will help prolong their lifespan.
- Store Properly: Store LiPo batteries in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight and extreme temperatures. For long-term storage, it’s recommended to keep them at around 40-60% charge.
- Inspect for Damage: Regularly inspect your LiPo batteries for any signs of damage like swelling, punctures, or leaks. If you notice any of these, stop using the battery immediately.
- Handle with Care: Avoid dropping or subjecting your LiPo batteries to physical shock.
Conclusion
LiPo batteries have revolutionized portable electronics and many other industries thanks to their lightweight design, flexibility, and high energy density. While they offer numerous advantages, it’s crucial for beginners to understand their limitations and safety considerations. By following proper charging, usage, and storage guidelines, you can ensure the longevity and safe operation of your devices powered by these remarkable batteries. As technology continues to advance, we can expect further innovations in LiPo battery technology, making them an even more integral part of our lives. If you have any questions or needs about our lipo cells, please feel free to contact us at info@landazzle.com.
FAQ
- Are LiPo batteries the same as regular lithium-ion batteries?
No, while both use lithium-ion technology, LiPo batteries use a polymer electrolyte (gel-like or solid) instead of a liquid electrolyte found in traditional lithium-ion batteries. This allows for more flexible shapes in LiPo batteries. - Are LiPo batteries safe to use?
Yes, when used correctly. It’s important to follow manufacturer guidelines for charging and handling. Built-in Battery Management Systems (BMS) in devices also help prevent overcharging and over-discharging.
- How long do LiPo batteries typically last?
The lifespan of a LiPo battery is usually measured in charge-discharge cycles. A typical range is between 300 to 500 cycles, but this can vary depending on usage patterns and care. - How should I charge my LiPo battery?
Always use a charger specifically designed for LiPo batteries. Follow the charger’s instructions and avoid overcharging. Most LiPo chargers will indicate when the battery is fully charged.
- What is the best way to store LiPo batteries when not in use?
Store them in a cool, dry place, away from extreme temperatures (ideally between 68°F and 77°F or 20°C to 25°C). For long-term storage, aim for a charge level between 40% and 60%. - What should I do if my LiPo battery starts to swell?
If a LiPo battery swells, immediately stop using and charging it. This is a sign of potential damage and a safety risk. Handle it with caution, and dispose of it responsibly according to local regulations for hazardous materials.