Table of Contents
Lithium Polymer batteries have become the preferred power source for modern electronic devices. Their lightweight design, high energy density, and flexible form factor make them ideal for applications where space, weight, and performance are critical. However, when choosing a LiPo battery, understanding its specifications is essential. Terms like voltage, capacity, discharge rate (C-rating), and size are more than just numbers on a label — they determine how your device performs, how long it runs, and how safely it operates.
In this guide, we’ll break down everything you need to know about LiPo battery specifications. You’ll learn what each specification means, how to interpret battery labels, and how different parameters affect performance and lifespan.
What are Lipo Battery Specifications?
LiPo battery specifications describe the key electrical and physical parameters that define how a lithium polymer battery performs, delivers power, and fits into a device. These specifications are printed on the battery label or datasheet and serve as a technical summary of the battery’s capabilities. Understanding these details allows engineers, product designers, and users to ensure compatibility, safety, and optimal performance.
A typical LiPo battery label includes information such as:
- Voltage (V): Indicates the nominal voltage of each cell and the total pack voltage.
- Capacity (mAh): Represents the total charge the battery can store — the higher the capacity, the longer the run time.
- Discharge Rate (C-Rating): Defines how quickly the battery can safely deliver current without overheating or damaging the cells.
- Number of Cells (S): Shows how many LiPo cells are connected in series (e.g., 3S = 3 cells = 11.1V nominal voltage).
- Dimensions and Weight: Determines the physical fit and suitability for compact or lightweight designs.
- Connector Type: Identifies the interface used to connect the battery to a device or charger.
For example, a LiPo battery labeled “3S 11.1V 2200mAh 25C” tells you it’s a 3-cell pack with a nominal voltage of 11.1 volts, a capacity of 2200mAh, and a maximum continuous discharge rate of 25C.
Lipo Battery Capacity
The capacity of a LiPo battery, usually measured in milliamp-hours (mAh) or amp-hours (Ah), represents how much electrical charge the battery can store. In simple terms, it indicates how long your device can operate before the battery needs to be recharged.
1 Ah (amp-hour) = 1000 mAh (milliamp-hours).
For example, a 2200mAh LiPo battery can theoretically deliver 2200 milliamps (2.2 amps) of current for one hour before it’s depleted.
In practical use, the higher the capacity, the longer the running time — but this comes with trade-offs. A larger capacity LiPo battery generally means increased size and weight, which can affect the overall design and balance of your device. This is especially critical for drones, robotics, and portable electronics, where every gram matters.
Lipo Battery Voltage
LiPo batteries can contain multiple cells connected in series, which increases the total voltage of the pack. The number of cells is represented by “S”:
- 1S = 3.7V
- 2S = 7.4V
- 3S = 11.1V
- 4S = 14.8V
- 6S = 22.2V
Generally, higher voltage packs can deliver greater power output (since power = voltage × current) and are preferred for applications that require more speed, torque, or thrust — such as drones, RC vehicles, and electric tools.
1.Nominal Voltage
This is the average operating voltage of a single LiPo cell during normal discharge.
- Typically 3.7V per cell (or 3.8V–3.85V for high-voltage LiPo cells).
It serves as the standard reference when designing electronic systems.
2.Fully Charged Voltage
The maximum voltage a cell reaches when it is fully charged.
- Usually 4.2V per cell (up to 4.35V–4.4V for high-voltage types).
Exceeding this voltage can cause overcharging and potential damage.
3.Fully Discharge Voltage
The lowest voltage a LiPo cell should safely reach during discharge.
- Generally 3.0V–3.2V per cell.
Discharging below this range may lead to over-discharge damage and capacity loss.
4.Cut-off Voltage
This is the minimum voltage level set by the BMS or ESC to stop discharge automatically and protect the battery.
- Typically 3.0V per cell.
It prevents deep discharge and prolongs battery life.
5.Storage Voltage
The recommended voltage for long-term storage of LiPo batteries.
- Usually 3.7V–3.85V per cell.
Keeping LiPo batteries at this level helps prevent both over-discharge and aging caused by full charge.
Discharge Specifications of a LiPo Battery
The discharge specifications of a LiPo battery define how much current the battery can safely deliver to a device during operation. These ratings are critical because they directly affect performance, heat generation, and battery lifespan. The main measure of discharge capability is the C-rating — a key specification you’ll find on every LiPo battery label.
1.C-rating
The C-rating represents the maximum continuous discharge rate relative to the battery’s capacity. It indicates how quickly the stored energy can be released without damaging the cells.
To calculate the maximum continuous discharge current, multiply the battery’s capacity (in amp-hours) by the C-rating:
Max Continuous Current (A)=Capacity (Ah)×C-rating
For example, a 2200mAh (2.2Ah) LiPo battery with a 25C rating can safely deliver:
2.2 × 25 = 55A continuous discharge current.
2.Burst Discharge Rate
In addition to the continuous C-rating, many LiPo batteries also specify a burst discharge rate (e.g., 25C/50C). The burst rating defines the short-term maximum current the battery can deliver for a few seconds (typically 5–10 seconds) to handle momentary power surges — for example, during drone takeoff or acceleration. However, operating at burst levels for too long can cause overheating and shorten the battery’s lifespan.
3.Discharge Rate Curve of Lipo Battery
The discharge rate curve illustrates how a LiPo battery’s voltage changes over time (or capacity) when discharged at different current rates, also known as C-rates. Understanding this graph is crucial for evaluating a battery’s performance, efficiency, and stability under various load conditions.
The chart below shows the voltage vs. capacity curves of a LiPo cell tested at 0.2C, 0.5C, 1C, 2C, and 3C discharge rates at 25°C, with a cutoff voltage of 3.0V.
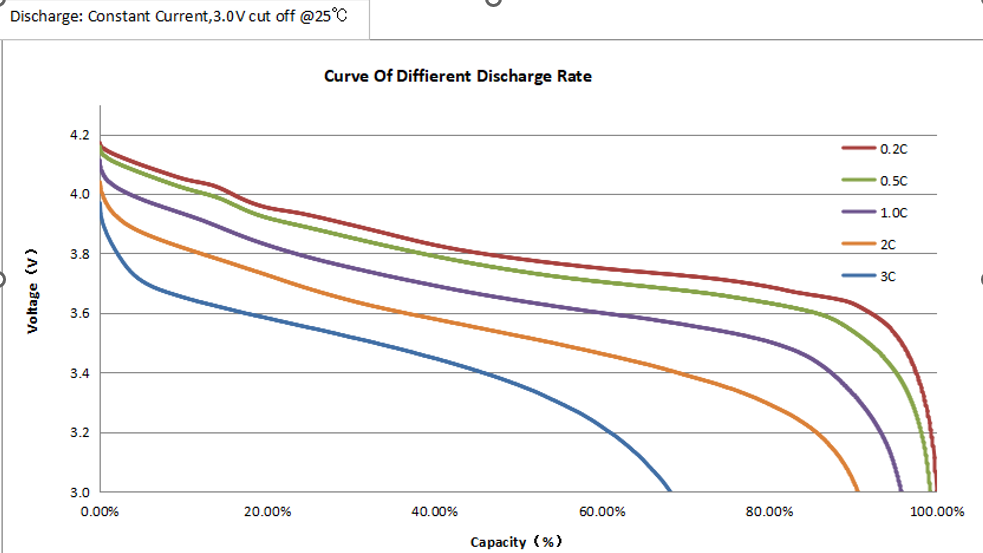
How to Read the Discharge Curve
- Voltage Axis (Y-axis):
Represents the battery’s output voltage (in volts). The higher the line stays during discharge, the better the voltage stability. - Capacity Axis (X-axis):
Indicates the percentage of the battery’s usable capacity as it discharges from 100% (fully charged) to 0% (cutoff). - Different Curves (0.2C to 3C):
Each line represents a different discharge rate.- At lower C-rates (e.g., 0.2C, 0.5C), the voltage remains more stable throughout discharge, indicating higher efficiency and lower internal losses.
- At higher C-rates (e.g., 2C, 3C), the voltage drops more quickly because the internal resistance causes greater voltage sag and heat generation.
- Cutoff Region:
Near the end of the discharge (around 90–100% capacity), the voltage drops sharply. This area marks the end of usable energy. Continuing to discharge beyond this point (below 3.0V) can permanently damage the battery.
Charge Specifications of a LiPo Battery
The charge specifications of a LiPo battery define how the cell is charged safely and efficiently to achieve full capacity without degrading its lifespan. Unlike conventional battery types, LiPo batteries require precise charging control, typically using a CC–CV (Constant Current – Constant Voltage) charging method.
The chart below illustrates a LiPo cell’s charging characteristic curve at 25 ± 5 °C, under a charge condition of 0.5C to 4.2V with a 0.05C cutoff current.

1. Charging Phases: CC–CV Mode
A LiPo battery is charged in two main stages:
- Constant Current (CC) Stage:
During the initial phase, the charger supplies a steady current (in this example, 0.5C). The battery voltage gradually rises from around 3.0V to 4.2V as the battery stores energy. This stage typically restores about 70–80% of the total capacity. - Constant Voltage (CV) Stage:
Once the cell voltage reaches 4.2V, the charger switches to a constant voltage mode. The charging current then begins to decrease gradually, allowing the remaining 20–30% of the capacity to be filled safely. The process ends when the current drops to the cutoff level (usually 0.05C), indicating full charge.
This dual-phase method prevents overcharging, which can lead to cell swelling, electrolyte breakdown, or even thermal runaway.
2. Understanding the Curve
- The blue line (Voltage) shows a smooth increase until it stabilizes at 4.2V during the CV stage.
- The red line (Current) remains constant initially and then drops sharply as the battery approaches full charge.
- The gray line (Capacity) rises progressively, reaching 100% when the cutoff condition is met.
This curve demonstrates how charging speed slows down near full capacity — a design that protects the cell and ensures long-term stability.
Cycle Life of Lipo Battery
Cycle Life tells you how many charge-discharge cycles a battery can undergo before it degrades significantly. A cycle is counted when you use 100% of the battery’s capacity, which can happen over multiple uses.
A battery is typically considered to have reached its end of life when its capacity drops to 80% of its original, new capacity.
How to Read the Cycle Life Curve
The chart below shows this degradation visually:
- Y-Axis (Capacity Retention %): Shows the battery’s remaining capacity.
- X-Axis (Cycle Life – Times): Shows the number of cycles completed.

How to interpret it:
- Start from the top left: a new battery has 100% capacity.
- The line slopes downward as the number of cycles increases, meaning the battery slowly loses its ability to hold a full charge.
- Find where the curve meets the 80% capacity line. The number on the bottom axis at that point is the battery’s rated cycle life.
In short, a higher cycle life means a longer-lasting battery. Note that using your battery hard (high discharge rates, extreme temperatures) can make it degrade faster than the chart shows.
Internal Resistance of Lipo Battery
Internal resistance (IR) is a crucial parameter that affects the performance, efficiency, and safety of a LiPo battery. It refers to the opposition within the battery that restricts the flow of current when the battery is discharging or charging. Lower internal resistance means the battery can deliver higher currents more efficiently, while higher resistance leads to voltage drops, heat generation, and reduced performance.
Why Internal Resistance Matters
Voltage Drop Under Load: High internal resistance causes a noticeable voltage drop when the battery is supplying current to a device, which can reduce the effective power output.
Heat Generation: Energy lost due to internal resistance is converted into heat. Excessive heat can shorten battery life, degrade cell chemistry, or in extreme cases, cause thermal runaway.
Performance in High-Drain Applications: Devices such as drones, RC cars, and high-power electronics rely on low-resistance batteries to deliver consistent bursts of current without significant voltage sag.
Energy Density of Lipo Battery
Energy density is one of the most important specifications when evaluating LiPo batteries. It refers to the amount of energy a battery can store relative to its weight (gravimetric energy density, measured in Wh/kg) or volume (volumetric energy density, measured in Wh/L). High energy density allows devices to run longer on a single charge while keeping the battery compact and lightweight—an essential feature for drones, wearable devices, RC vehicles, and other portable electronics.
Gravimetric vs. Volumetric Energy Density
Gravimetric Energy Density (Wh/kg): Indicates how much energy is stored per kilogram of battery. A higher value means the battery provides more power without significantly increasing weight.
Volumetric Energy Density (Wh/L): Measures the energy stored per liter of battery volume. This is critical when the physical space for a battery is limited, such as in smartphones or compact drones.
Conclusion
By understanding these key specifications, users can choose, operate, and maintain LiPo batteries to achieve optimal performance and extended lifespan. Always adhere to manufacturer guidelines for safe handling and usage.
As a leading custom LiPo battery manufacturer, LanDazzle provides tailor-made battery solutions designed to meet the unique requirements of different applications. Our batteries offer high energy density, long cycle life, and customizable options for discharge rates, form factors, and fast-charging capabilities, ensuring reliable performance in any scenario.
For inquiries or custom battery solutions, please contact us.
Email: info@landazzle.com
Whatsapp: +8618938252128

