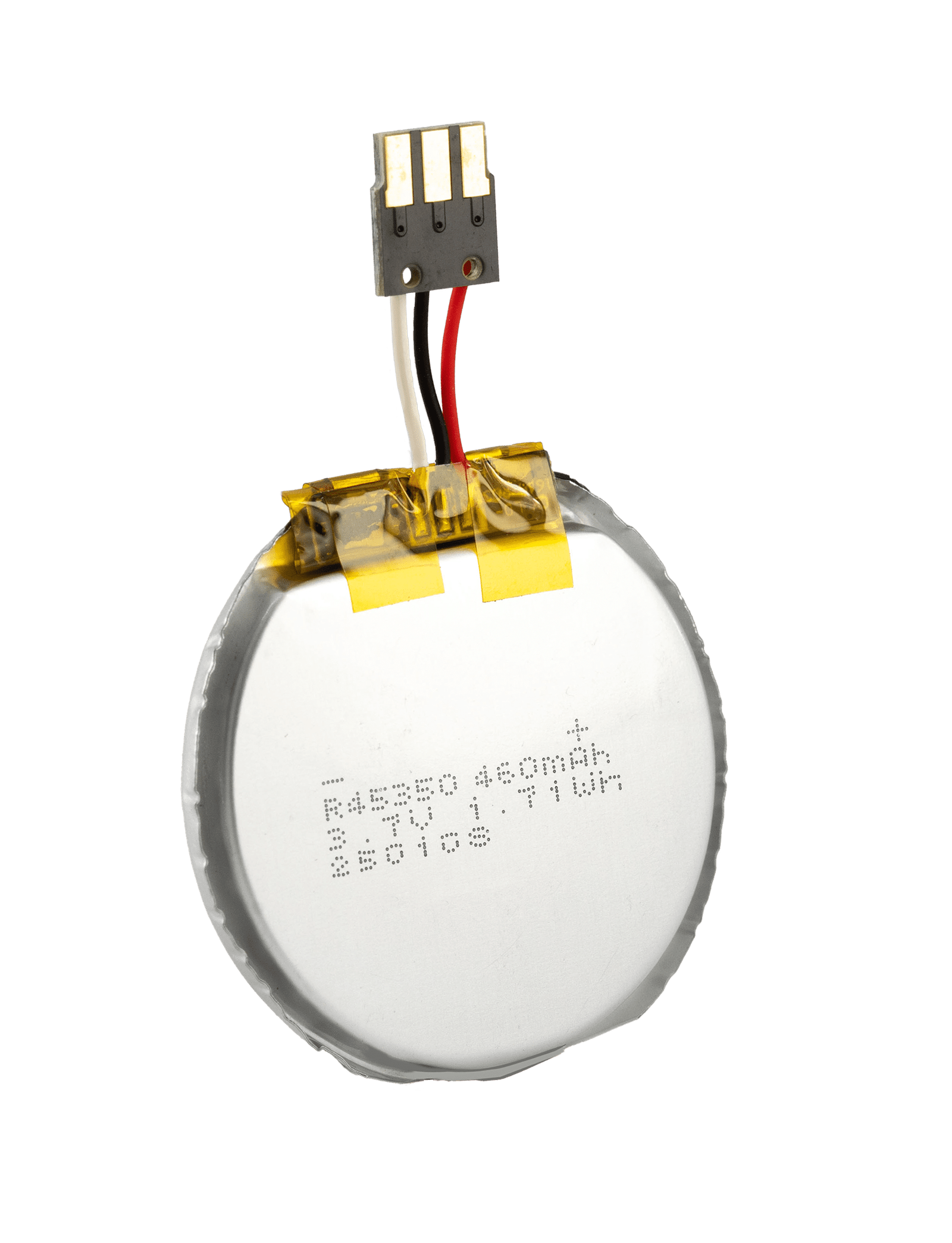
In an era defined by sleek smartphones, powerful drones, and ever-thinner laptops, the silent enabler of this technological revolution is often overlooked: the battery. Specifically, the lithium-polymer battery has emerged as a cornerstone of modern portable electronics. But what exactly is a Li-polymer battery, and how has it become so integral to our daily lives? This comprehensive guide will unpack everything you need to know about this remarkable power source, from its inner workings to its future potential.
Understanding the Basics: What is a Li-Polymer Battery?
Defining the Li-Polymer Battery
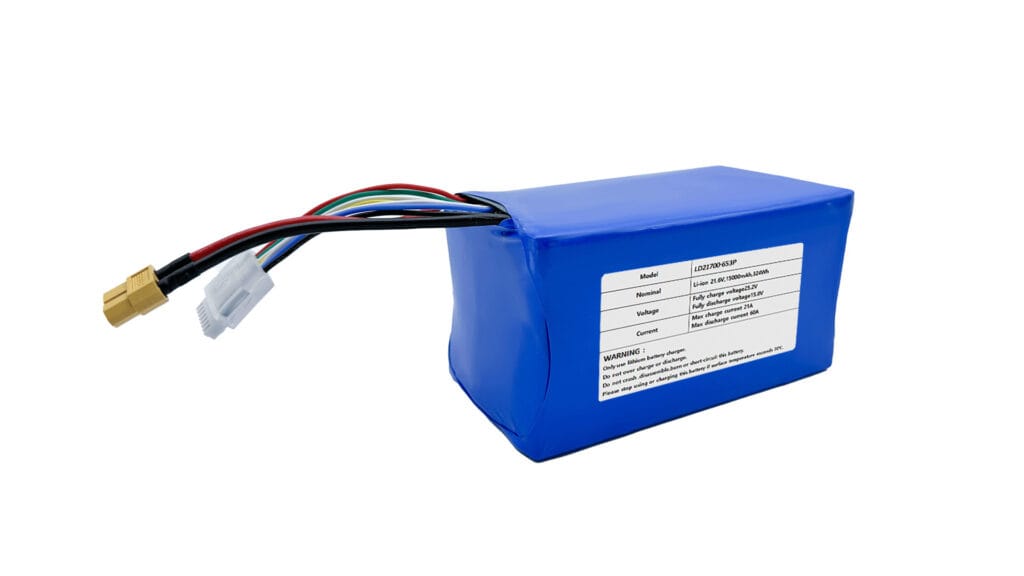
A lithium-polymer battery, commonly abbreviated as LiPo, Li-poly, or LIP, is a type of rechargeable battery. More accurately, it is a lithium-ion polymer battery, a member of the broader lithium-ion battery family. What sets it apart is its use of a polymer electrolyte instead of the liquid electrolyte found in conventional lithium-ion cells. This electrolyte is a gel-like or semi-solid substance, which is the key to many of its unique properties.
How Do Li-Polymer Batteries Work?
At its core, a Li-polymer battery operates on the same principle as other lithium-ion batteries: the movement of lithium ions. During discharge (when you’re using your device), lithium ions travel from the negative electrode (anode) through the polymer electrolyte to the positive electrode (cathode), releasing a flow of electrons that power your device. When you charge the battery, an external power source forces these lithium ions to move back from the cathode to the anode, where they are stored, ready for the next use. The polymer electrolyte acts as the medium for this ionic traffic, while a separator prevents the anode and cathode from touching and causing a short circuit.
The Anatomy of a Li-Polymer Battery
Imagine a sandwich. The “bread” slices are the anode and cathode, typically made of coated foils. The “filling” is the polymer electrolyte and the separator. This entire assembly is then encased in a flexible, pouch-like aluminum-plastic film. This pouch design is a defining feature of LiPo batteries, allowing them to be made in various shapes and sizes, a significant advantage in the design of compact and unconventionally shaped electronic devices.
The Pros and Cons of Li-Polymer Batteries
Li-polymer batteries offer a compelling set of advantages, but they also come with certain trade-offs.
Advantages of Li-Polymer Batteries
- Fattore di forma flessibile: Their pouch-like construction allows them to be manufactured in very thin, lightweight, and customizable shapes. This design freedom is a boon for engineers creating everything from credit-card-sized power banks to batteries that fit snugly within the frame of a drone.
- Maggiore densità energetica: For their size and weight, Li-polymer batteries can pack a significant amount of power. This high energy density is crucial for devices where both long battery life and a slim profile are paramount.
- Lower Profile: The absence of a rigid metal casing allows for a much thinner battery, contributing to the sleek design of modern smartphones and laptops.
- Improved Safety (in some respects): While no battery is without risks, the semi-solid electrolyte in Li-polymer batteries makes them less prone to leaking than their liquid electrolyte counterparts.
Disadvantages and Limitations
- Costo più elevato: The manufacturing process for Li-polymer batteries is more complex and expensive than for traditional cylindrical Li-ion cells, which can translate to a higher cost for the end consumer.
- Sensitivity to Mishandling: The flexible pouch, while advantageous for design, makes the battery more susceptible to damage from punctures or excessive pressure. Mishandling can lead to a dangerous condition known as thermal runaway.
- Lower energy density and cycle life than some rigid Li-ion cells: While generally offering good energy density, some high-performance cylindrical Li-ion cells can outperform them in this regard.
Li-Polymer vs. Li-ion: What’s the Difference?
The terms “lithium-polymer” and “lithium-ion” are often used interchangeably, leading to confusion. While a Li-polymer battery is a type of Li-ion battery, there are key distinctions.
The Core Distinction: Electrolyte
The fundamental difference lies in the electrolyte. A traditional lithium-ion battery uses a liquid electrolyte soaked into a separator. A lithium-polymer battery, as we’ve discussed, uses a semi-solid or gel-like polymer electrolyte.
A Head-to-Head Comparison
| Caratteristica | Polimeri di litio (LiPo) | Lithium-Ion (Li-ion) (Cylindrical/Prismatic) |
|---|---|---|
| Fattore di forma | Flexible pouch, highly customizable | Rigid cylindrical or prismatic metal case |
| Densità di energia | Good to high | Can be very high in premium cells |
| Sicurezza | Prone to swelling if damaged or overcharged | Can fail more violently if punctured |
| Costo | Generally more expensive | More cost-effective to mass-produce |
| Ciclo di vita | Typically 300-500 cycles | Can exceed 500-1000+ cycles |
| Common Uses | Smartphones, drones, wearables | Power tools, EVs, laptops (in packs) |
The choice between Li-polymer and Li-ion is a classic engineering trade-off. For a device that needs to be as thin and light as possible, like a high-end smartphone, a custom-shaped Li-polymer battery is the clear winner. For applications that demand ruggedness and a very high number of charge cycles, like a cordless power drill, cylindrical Li-ion cells are often preferred.
Common Applications of Li-Polymer Batteries
The unique characteristics of Li-polymer batteries have led to their adoption in a wide array of applications.
Powering Our Portable World
Take a look at the electronic devices you use every day. Your smartphone, tablet, laptop, and even your wireless earbuds likely contain a Li-polymer battery. Their ability to be molded into thin, flat shapes has been instrumental in the trend towards ever-slimmer and more portable gadgets. Power banks, the lifelines of our mobile existence, also predominantly use Li-polymer cells to maximize capacity while maintaining a pocket-friendly size.
High-Performance Hobbies and Industries
In the world of radio-controlled (RC) hobbies, particularly drones and high-performance RC cars, Li-polymer batteries are the gold standard. They can deliver the high burst of current (high C-rating) needed for powerful motors while keeping the overall weight of the vehicle low, which is critical for flight and agility. Beyond hobbies, Li-polymer batteries are found in critical applications such as medical devices, where reliability and a compact form factor are essential, and in military equipment. They are also being increasingly used in the electric vehicle (EV) market, particularly in pouch cell configurations.
Safety, Handling, and Lifespan of Li-Polymer Batteries
With great power comes the responsibility of safe handling. Li-polymer batteries are generally safe when used correctly, but it’s crucial to be aware of the risks and best practices.
Understanding the Risks: Swelling and Punctures
One of the most well-known issues with Li-polymer batteries is “swelling” or “puffing.” This occurs when the battery’s internal cells degrade, often due to overcharging, overheating, or physical damage. This degradation can lead to the generation of gas, which causes the flexible pouch to swell. A swollen battery is a serious safety hazard and should never be used. A puncture to a LiPo battery, whether swollen or not, can cause a short circuit, leading to a rapid release of energy in the form of heat and potentially fire—a phenomenon known as thermal runaway.
Best Practices for Safe Charging and Storage
- Utilizzare il caricatore giusto: Always use a charger specifically designed for Li-polymer batteries. These chargers are programmed with the correct charging algorithms to prevent overcharging.
- Never Leave Charging Unattended: While modern chargers have safety features, it’s always wise to monitor charging batteries and never charge them overnight.
- Charge in a Safe Area: Charge your LiPo batteries on a non-flammable surface, away from combustible materials. A LiPo-safe charging bag is a recommended safety accessory.
- Conservare correttamente: Store Li-polymer batteries in a cool, dry place. For long-term storage, it’s best to keep them at about 50% charge.
Maximizing the Lifespan of Your LiPo Battery
- Evitare le scariche profonde: Constantly running your battery down to zero can shorten its life. Try to recharge it before it gets critically low.
- Don’t Store at Full or Empty Charge: Leaving a LiPo battery fully charged or fully discharged for extended periods can accelerate its degradation.
- Keep it Cool: Heat is the enemy of all batteries. Avoid leaving your devices in hot cars or in direct sunlight for prolonged periods.
- Recognize the Signs of Failure: A swollen battery is the most obvious sign of failure. Other indicators include a significant decrease in runtime or the battery getting unusually hot during charging or use.
For more in-depth information on battery technology, the U.S. Department of Energy explains batteries in great detail, offering a wealth of knowledge for those looking to delve deeper.
Conclusione
The lithium-polymer battery is a marvel of modern chemistry and engineering. Its unique combination of a flexible form factor and high energy density has reshaped the landscape of consumer electronics and beyond. While they require careful handling and have a finite lifespan, their benefits have made them an indispensable power source. As technology continues to advance, we can expect to see even more impressive developments in battery technology, with research into solid-state batteries promising even greater safety and performance. For now, the humble Li-polymer battery remains the silent, powerful heart of our most cherished devices.
A Lan Dazzle, we specialize in designing and manufacturing custom Li Polymer batteries to match the exact specifications of your product—no matter how compact, curved, or unconventional the form factor may be. Whether you’re building next-gen wearables, medical devices, drones, or smart consumer electronics, our team ensures optimal battery performance, safety, and seamless integration. From concept to mass production, we provide reliable engineering support and fully customized battery solutions to power your innovation.
📩 Contattateci oggi stesso a info@landazzle.com to discover how we can bring your product to life with a battery built just for it.
Domande frequenti (FAQ)
1. Are lithium-polymer batteries better than lithium-ion? Not necessarily “better,” but different. Li-polymer batteries offer more flexibility in shape and size, making them ideal for slim devices. Li-ion batteries, particularly in cylindrical form, can offer higher energy density and a longer cycle life. The “better” choice depends on the application.
2. Can a swollen Li-polymer battery be fixed? No. A swollen LiPo battery is a sign of internal damage and a potential safety hazard. It should be safely discharged and disposed of immediately at a proper recycling facility. Do not attempt to use or puncture a swollen battery.
3. Can I use a regular Li-ion charger for a Li-polymer battery? It is crucial to use a charger specifically designed for Li-polymer batteries. While the charging principles are similar to Li-ion, LiPo batteries have specific voltage and current requirements. Using the wrong charger can lead to overcharging, damage, and even fire.
4. What is the ‘C’ rating on a LiPo battery? The ‘C’ rating indicates the maximum safe continuous discharge rate of the battery. For example, a 1000mAh battery with a 20C rating can theoretically deliver 20 * 1000mA = 20,000mA or 20A. A higher C rating is important for high-performance applications like drones.
5. Are Li-polymer batteries bad for the environment? Like all batteries, Li-polymer batteries contain materials that can be harmful if not disposed of properly. However, they are generally considered more environmentally friendly than older battery technologies like nickel-cadmium. Recycling is essential to recover valuable materials and prevent pollution.
6. How do I safely dispose of a Li-polymer battery? Do not throw LiPo batteries in the regular trash. They should be taken to a designated battery recycling center or a household hazardous waste facility. Many electronics stores also have battery take-back programs.