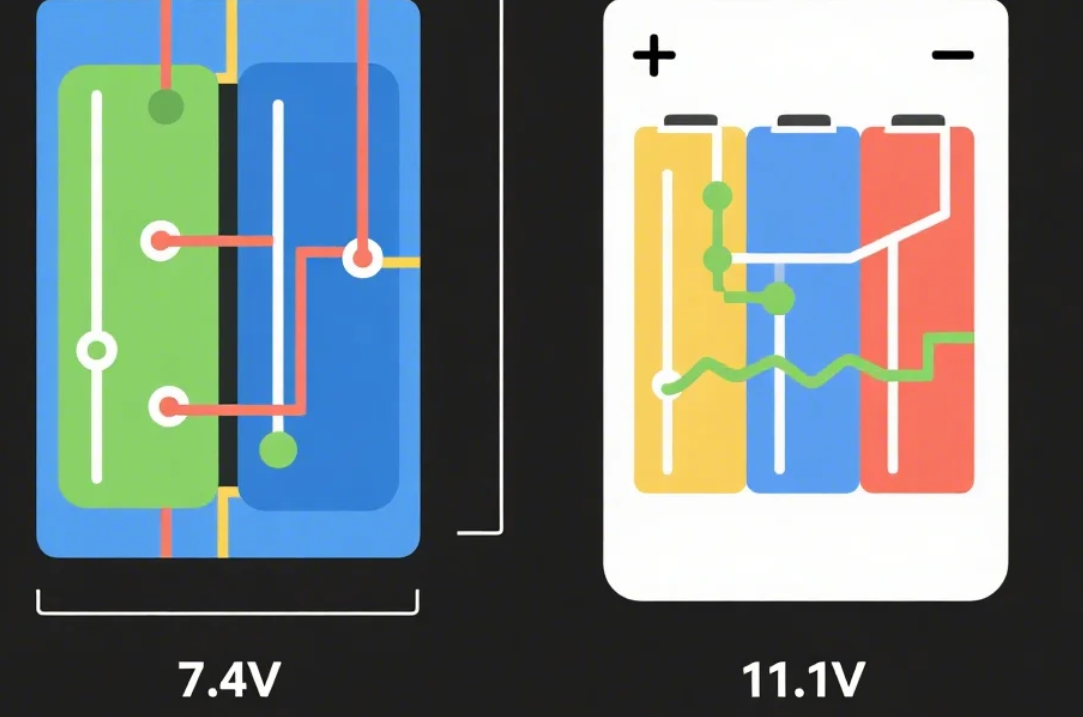
Introduction
Smart glasses are transforming how we interact with the world—combining displays, cameras, and sensors in ultra-compact frames. But behind these advanced features lies one crucial component: the battery. Choosing the right battery affects everything from device weight to runtime and safety. As form factors shrink, demand for thin, high-density, and safe power sources grows rapidly. Lithium polymer (LiPo) batteries are now the leading choice for most manufacturers.
Batteries Used in Smart Glasses
Smart glasses require batteries that are compact, lightweight, and capable of delivering stable performance in a very limited space. While several battery types have been explored in wearable electronics, only a few meet the unique demands of smart glasses. Here are the most commonly used battery types in this space:
1. Lithium Polymer (LiPo) Batteries
Lithium polymer batteries are currently the most widely used power source in smart glasses. They offer a slim profile, flexible form factors, and relatively high energy density—making them ideal for integration into thin, lightweight eyewear frames. Their customizable shapes also allow for seamless design adaptation, which is essential in miniaturized wearables.
2. Lithium-Ion (Li-ion) Batteries
Traditional cylindrical or prismatic lithium-ion batteries provide excellent energy density and long cycle life. However, their rigid structure and limited flexibility make them less suitable for compact smart glasses, unless used in modular or external designs. They are more commonly found in larger wearables or AR headsets.
3. Solid-State Batteries (Emerging)
Solid-state batteries are still in the early stages of commercial deployment but are gaining attention for their potential to deliver higher energy density and improved safety. With no liquid electrolyte, they can be made thinner and are less prone to overheating—key advantages for next-generation smart glasses. However, cost and scalability remain challenges.
4. Zinc-Air and Coin Cell Batteries (Limited Use)
In some ultra-light smart glasses or basic audio-enabled glasses, low-power coin cell or zinc-air batteries may be used to extend runtime with minimal weight. These are generally not rechargeable and are limited to simple devices with minimal power requirements.
Battery Comparison Table for Smart Glasses
| Battery Type | Energy Density | Size Flexibility | Rechargeable | Safety Level | Typical Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lithium Polymer | High | Very High | Yes | High | Most mainstream smart glasses |
| Lithium-Ion | Very High | Low | Yes | Moderate | Larger AR devices, external modules |
| Solid-State | Very High | Moderate | Yes | Very High | Future high-end smart glasses (R&D) |
| Coin Cell | Low | Small, fixed | No (mostly) | High | Basic audio glasses, low-power use |
| Zinc-Air | Low | Small, fixed | No | High | Hearing aids, ultra-light glasses |
Battery Design Challenges in Smart Glasses
Designing batteries for smart glasses involves several unique challenges due to the device’s compact size and complex functionality. Here are the key difficulties manufacturers and engineers face:
1. Limited Space and Thin Form Factor
Smart glasses must remain lightweight and comfortable for all-day wear. This means the battery has to fit into a very slim and irregularly shaped space inside the frame or temple arms. Achieving sufficient capacity without increasing bulkiness is a constant balancing act.
2. Weight Constraints
The battery contributes significantly to the overall weight of the glasses. Heavier batteries can cause discomfort and affect the user experience, so manufacturers prioritize lightweight materials and designs that minimize weight while maximizing power.
3. Heat Dissipation and Safety
Even small batteries generate heat during charging and discharging. In a device worn close to the skin and eyes, effective heat management is critical to prevent overheating and ensure user safety. Battery chemistry and protective circuitry play vital roles here.
4. Maintaining Long Runtime in Small Size
Smart glasses often incorporate power-hungry features like displays, cameras, sensors, and wireless communication. Delivering adequate runtime from a tiny battery requires high energy density cells and efficient power management strategies.
5. Flexible and Custom Shapes
Unlike phones or laptops, smart glasses have highly customized and curved designs. Batteries must be flexible or shaped to fit these contours without compromising structural integrity or performance.
6. Integration with Charging Methods
The battery must support charging methods compatible with the glasses design, such as fast charging, wireless charging, or magnetic connectors. Ensuring safe and efficient charging in a compact form is a technical challenge.
Performance & Safety Considerations
When it comes to smart glasses, battery performance and safety are paramount. Due to the close contact with the user’s skin and sensitive areas like around the eyes, batteries must meet strict standards:
-
High Energy Density: Batteries need to deliver enough power to support features such as AR displays, cameras, and wireless connectivity, all while maintaining a small size.
-
Stable Voltage Output: Consistent voltage is crucial to prevent device crashes or malfunctions during use.
-
Thermal Management: Batteries must minimize heat generation and efficiently dissipate any heat to avoid discomfort or damage.
-
Built-in Protection Circuits: Overcharge, over-discharge, short-circuit, and temperature protections are necessary to ensure long-term safety.
-
Compliance with Safety Standards: Certifications like UL, UN38.3, IEC, and RoHS confirm that batteries meet international safety and environmental requirements.
Customization Options for Smart Glasses Batteries
Given the diversity of smart glasses designs, off-the-shelf batteries often can’t meet all requirements. Custom battery solutions provide manufacturers with several advantages:
-
Shape and Size Customization: Batteries can be tailored to fit unique frame geometries and internal spaces, including curved or thin profiles.
-
Capacity and Voltage Adjustment: Custom packs can be designed to meet specific power and runtime needs without excess weight.
-
Connector and Interface Design: Custom terminals and protection circuits ensure seamless integration with the device’s electronics and charging system.
-
Enhanced Safety Features: Additional safety measures can be embedded depending on the use case and environmental conditions.
-
Branding and Packaging: Batteries can be labeled or packaged according to brand specifications for OEM products.
Partnering with a specialized battery manufacturer enables smart glasses developers to optimize their products for performance, comfort, and safety.
LanDazzle Custom Battery Solutions for Smart Glasses
As the smart glasses market continues to evolve, there is an increasing demand for custom battery solutions that cater to specific use cases, form factors, and design requirements. Lan Dazzle, a leading manufacturer of custom lithium-ion and lithium-polymer batteries, plays a key role in supplying high-quality, tailor-made batteries for smart glasses.
Why Customization Matters:
Custom batteries allow manufacturers to meet the exact power needs of their smart glasses products. This is especially important in the wearables market, where space and weight are at a premium. By partnering with a trusted custom battery manufacturer, companies can develop batteries that are not only high-performance but also cost-effective and optimized for specific designs.
Lan Dazzle’s extensive expertise in battery design and production ensures that clients receive batteries that meet their technical specifications while ensuring long-term reliability and performance.
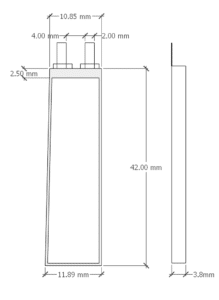
Future of Smart Glasses Batteries
Looking ahead, the future of smart glasses batteries holds exciting possibilities. Advances in battery chemistry, such as solid-state batteries, promise to offer higher energy densities, faster charging times, and safer usage. Additionally, innovations in energy harvesting technologies, such as solar-powered lenses, could extend battery life even further.
As smart glasses become more mainstream, battery technology will continue to play a crucial role in enhancing the user experience, driving more efficient, longer-lasting, and lighter batteries.
Conclusion
Smart glasses are revolutionizing the way we interact with technology, but their success depends heavily on the development of reliable and efficient batteries. Lithium-ion and lithium-polymer batteries are currently the most common solutions for powering these devices, but the future may hold even more innovative solutions. By partnering with custom battery manufacturers like Lan Dazzle, companies can ensure that their smart glasses are powered by the best possible battery technology tailored to their specific needs.